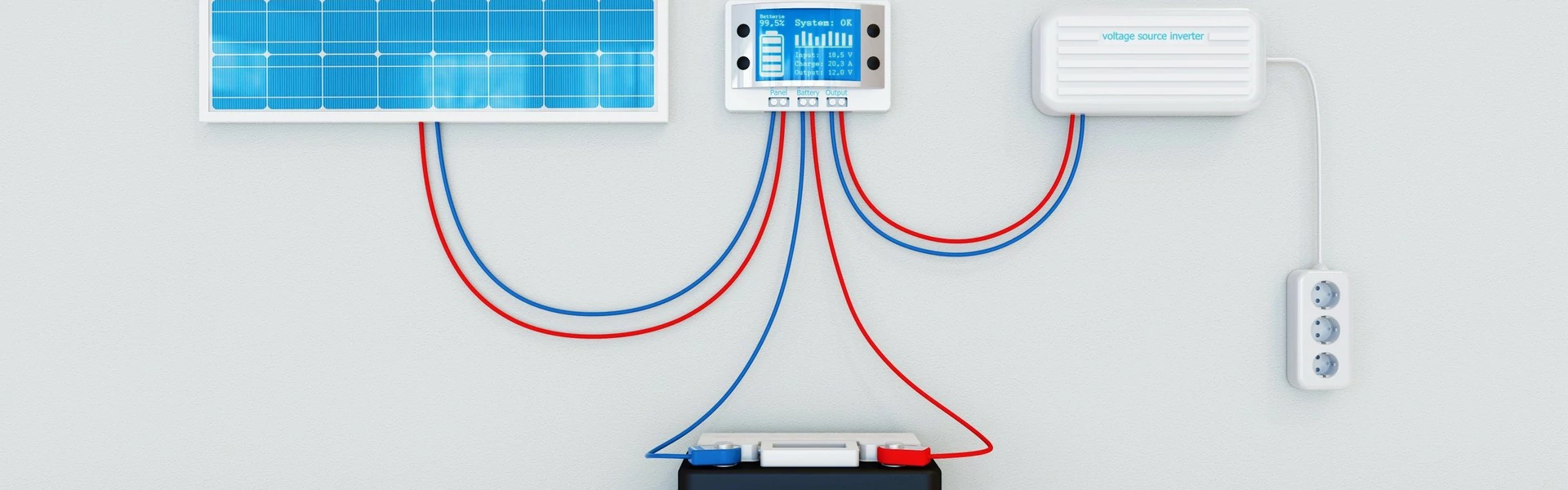
A highly integrated backup power solution for solar home energy...
solar inverter
Generally, the process of converting AC electrical energy into DC electrical energy is called rectification, the circuit that completes the rectification function is called the rectifier circuit, and the device that realizes the rectification process is called the rectifier equipment or rectifier. Correspondingly, the process of converting direct current energy into AC power is called inverter, the circuit that completes the inverter function is called the inverter circuit, and the device that realizes the inverter process is called the inverter equipment or inverter. Inverter is also known as power regulator, according to the use of inverter in photovoltaic power generation system can be divided into independent power supply and grid-connected two kinds. According to the waveform modulation mode, it can be divided into square wave inverter, step wave inverter, sine wave inverter and combined three-phase inverter.
For inverters used in grid-connected systems, they can be divided into transformer-type inverters and transformer-free inverters according to whether there is a transformer. There are many types of inverters, so special attention should be paid to the selection of machine types and capacities. Especially in solar power generation systems, the efficiency of photovoltaic inverters is an important factor in determining the capacity of solar cells and battery capacity.
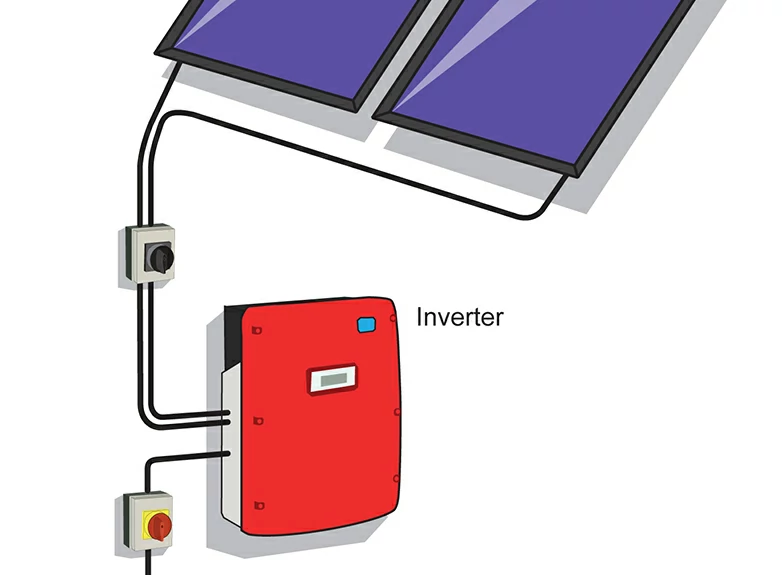
Principle and function of inverter
Definition of inverter
Inverter is a power regulation device composed of semiconductor devices, which is mainly used to convert DC power into AC power. The inverter is mainly composed of switching components such as transistors, and turns the DC input into the AC output by regularly making the switching components repeatedly ON - OFF (ON - OFF).
Working principle of inverter
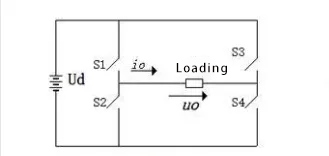
The single bridge inverter circuit in the following figure is taken as an example to illustrate its most basic working principles. In the figure, S1-S4 are the four arms of the bridge circuit, which are composed of power electronics and auxiliary circuits. When switches S1 and S4 are closed and S2 and S3 are turned off, the load voltage V0 is positive; When switches S2 and S3 are closed and S1 and S4 are off, the load voltage V0 is negative, and the waveform is shown in the figure. In this way, the direct current maintains the alternating current, and the frequency of alternating current can be changed by changing the switching frequency of the two groups of switches.
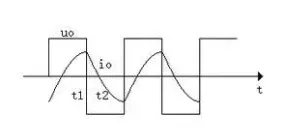
Of course, such a pure inverter output waveform generated by the on and off loop is not practical. Generally, it is necessary to use high-frequency pulse width modulation (SPWM), which is to narrow the voltage width near the two ends of the sine wave, widen the voltage width in the center of the sine wave, and always make the switching element act in one direction according to a certain frequency in half a cycle, so as to form a pulse wave train (pseudo-sine wave). The pulse is then passed through a simple filter to form a sine wave.
The inverter is generally composed of a booster circuit and an inverter bridge circuit. The boost circuit raises the DC voltage of the solar cell to the output control voltage required by the inverter, while the inverter bridge circuit converts the boosted DC to the AC voltage of the common frequency. The inverter bridge circuit is composed of inverter bridge, control logic and filter circuit, and the key electronic component is IGBT.
It is important to understand the main technical indicators of the inverter, because these indicators directly affect the performance, efficiency and applicability of the inverter. First of all, technical parameters such as the power capacity, efficiency and harmonic distortion of the inverter determine its performance in specific application scenarios, such as photovoltaic power generation, energy storage systems or electric vehicle charging. Secondly, understanding these indicators can help users choose the inverter that suits their needs and ensure that it can play the best performance in actual use. In addition, the reliability, response speed and protection function of the inverter are also related to the safety and stability of the system, which affects the operation of the entire power system. Therefore, mastering the main technical indicators of the inverter can not only improve the overall efficiency of the system, but also provide a strong basis for later maintenance and troubleshooting.
There are many ways to classify inverters, such as: according to the number of phases of the output AC voltage of the inverter, it can be divided into single-phase inverters and three-phase inverters; According to the different types of semiconductor devices used in the inverter, it can be divided into transistor inverter, thyristor inverter and thyristor inverter that can be turned off. According to the different principle of inverter circuit, it can also be divided into self-excited oscillation inverter, step wave superimposed inverter and pulse width modulation inverter. According to the application in the grid-connected system or off-grid system can be divided into grid-connected inverter and off-grid inverter and so on.
The design and selection of inverters as the core need to find the balance point between the total power generation and the total cost within the life cycle of the photovoltaic system, but also consider the requirements of grid access, such as fault crossing ability, power quality, grid adaptability and so on. According to the characteristics of various inverters, combined with the actual situation of the applied photovoltaic power station, scientific and reasonable selection is carried out from the aspects of grid friendliness, high return on investment, convenient construction and maintenance.
The main application areas of inverters include user solar power generation, transportation power, communication/communication field, petroleum, Marine, meteorological field, household lighting power supply, photovoltaic power stations, solar buildings.

Home energy storage product series
A lithium battery pack for home energy storage systems, which is compatible with solar panels and the sun The inverter can work together with the power grid to power household appliances, and it can also be used as a For off grid systems.
Extended reading
THE ESSC Brand promise
Global supply
Our products sell well all over the world, covering many countries and regions, through the global logistics network, to provide customers with convenient purchasing experience.
Rigorous quality
We adhere to the highest quality control standards to ensure every product meets industry regulations and customer expectations, earning trust through consistent excellence.
Excellent service
With a customer-centric approach, we provide prompt responses, professional support, and personalized services, aiming to deliver the best user experience and long-term value.