Package Mylar Wrap Mylar film around the bare core and...
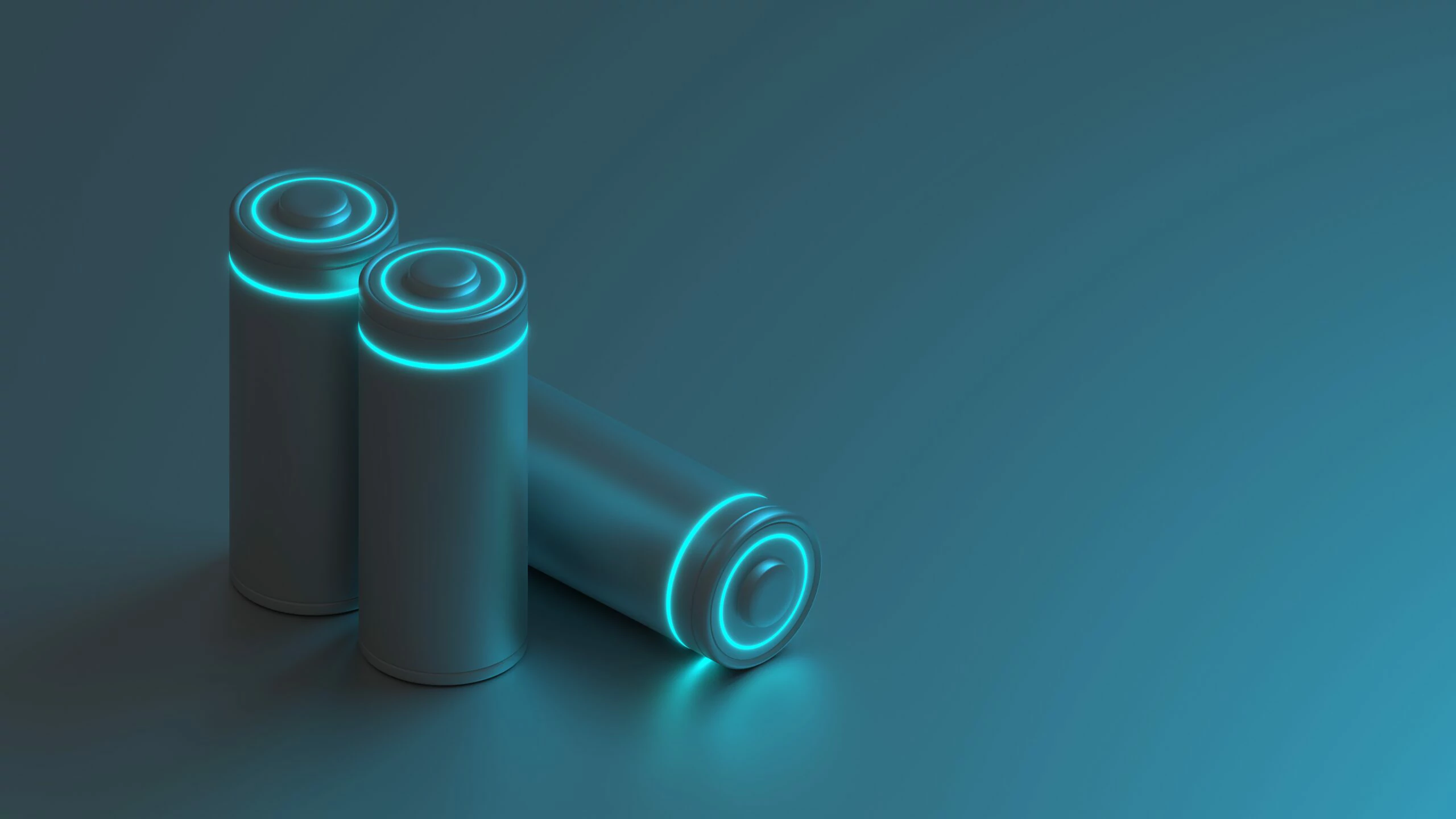
Charge and discharge ratio of a battery pack
In the field of battery technology, the charge and discharge rate (C-rate) is an important parameter, which describes the ability of a battery to be charged or discharged per unit time. Understanding the charge and discharge rate is essential for users to effectively manage battery performance and application scenarios. In this paper, the definition, calculation method, influencing factors and importance in practical application of charge and discharge rate will be discussed in depth.
definition
Charge and discharge ratio is usually represented by the letter "C" and is defined as the proportion of battery capacity, specifically refers to:
1C: means that the battery is charged or discharged at the rate of its rated capacity. For example, if the battery has a capacity of 1000 milliamperes (mAh), charging and discharging at 1000 milliamperes is 1C.
0.5C: indicates that the battery is charged and discharged at a rate of half its rated capacity, which is a current of 500 mA.
2C: Then indicates that the battery is charged and discharged at twice the rate of its rated capacity, which is 2000 mA current.
With such a definition, it is possible to clearly describe the charging and discharging ability of the battery in a specific time period.
Calculation method of C multiplier
The calculation of charge and discharge ratio is relatively simple, and the formula is as follows:
[C_{\text{rate}} = \frac{I}{C}]
Among them:
(I) is the charging and discharging current (unit: amperes, A);
(C) is the rated capacity of the battery (in ampere-hours, Ah).
For example, if the capacity of a battery is 2Ah and the current is discharged at 3A, the C ratio is:
[C_{\text{rate}} = \frac{3A}{2Ah} = 1.5C]
Similarly, if A current of 0.5A is charged, the C ratio is as follows.
[C_{\text{rate}} = \frac{0.5A}{2Ah} = 0.25C]
Influencing factors of charging and discharging rate
The charging and discharging rate is affected by many factors, including:
Battery chemistry: Batteries with different chemical compositions (such as lithium-ion batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries, lead-acid batteries, etc.) have different performance characteristics in charge and discharge rate. Lithium-ion batteries generally have high charge and discharge ratios, which are suitable for fast charge and discharge requirements.
Temperature: The charging and discharging ability of the battery changes at high and low temperatures. Low temperatures usually limit the discharge capacity of the battery, while high temperatures can lead to overheating and affect battery safety.
Battery aging: As the battery life increases, its internal chemical reactions and physical state changes may also cause the C-multiplications to decrease.
Charger and circuit design: The design of the charger and the layout of the circuit will also affect the actual charging and discharging multiplier, and a more efficient charging design can achieve a higher C-multiplier.
Application of charging and discharging rate
Charge and discharge ratio plays an important role in a variety of application scenarios:
Electric vehicle: High C rate battery can achieve fast charging, reduce charging time, but also support high power discharge, increase the acceleration performance of the vehicle.
Energy storage systems: In renewable energy (such as solar and wind) energy storage systems, C-multiplier can affect the rapid release of energy and storage efficiency, and optimize power dispatch.
Portable electronic devices: In smart phones, laptops and other devices, the appropriate C ratio not only affects the charging time of the battery, but also relates to the battery life performance of the device.
Robotics and power tools: For applications that require high power and fast response, such as power tools and drones, high-C-rate batteries can provide the necessary power support.
Conclusion
Charge and discharge ratio (C) is an important indicator of battery pack performance, which affects the charging speed, discharging ability of the battery and the choice of application scenarios. Understanding and applying the concept of C-multiplier can help users better manage the use and maintenance of batteries and improve the efficiency and safety of devices. With the continuous development of technology, future batteries will be able to achieve higher C-multiplier and provide more powerful energy support for various applications.
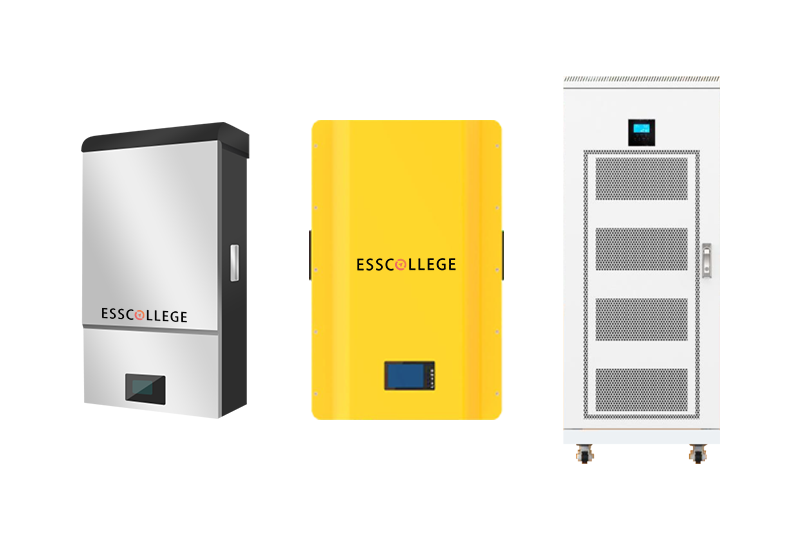

Home energy storage product series
A lithium battery pack for home energy storage systems, which is compatible with solar panels and the sun The inverter can work together with the power grid to power household appliances, and it can also be used as a For off grid systems.
Extended reading
Introduction of sealing material for joint parts of battery shell
Introduction of sealing material for joint parts of battery shell...
THE ESSC Brand promise
Global supply
Our products sell well all over the world, covering many countries and regions, through the global logistics network, to provide customers with convenient purchasing experience.
Rigorous quality
We adhere to the highest quality control standards to ensure every product meets industry regulations and customer expectations, earning trust through consistent excellence.
Excellent service
With a customer-centric approach, we provide prompt responses, professional support, and personalized services, aiming to deliver the best user experience and long-term value.