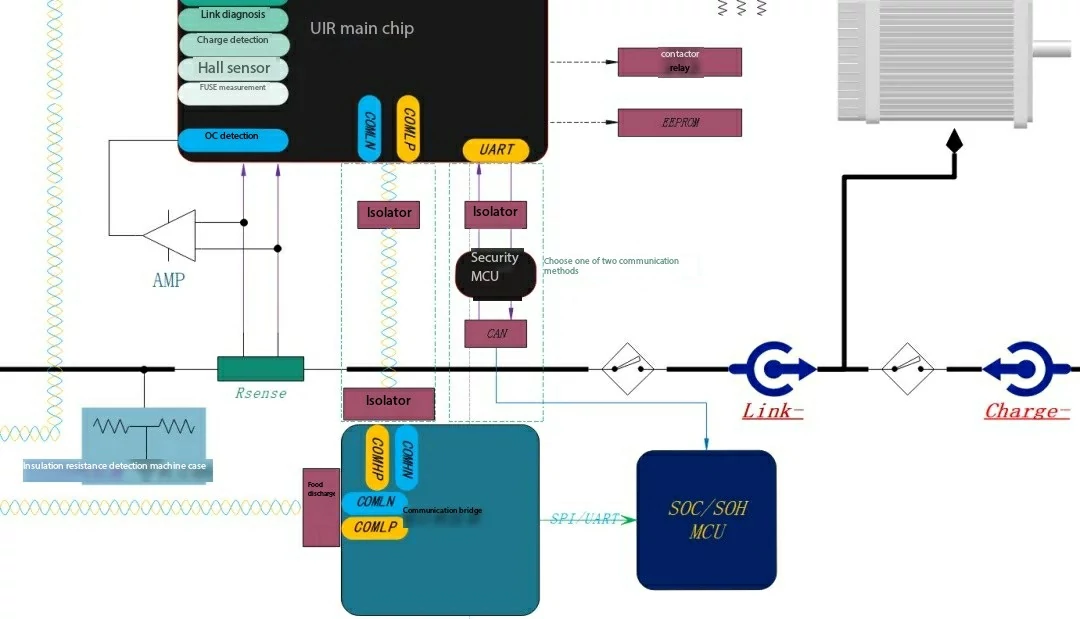
BCU Introduction: The BCU is the brain of the BMS,...
BMS protection working principle
BMS includes control IC, MOS switch, Fuse, NTC thermistor, TVS transient voltage suppressor, capacitor and memory, etc. Its specific form is shown in the figure:
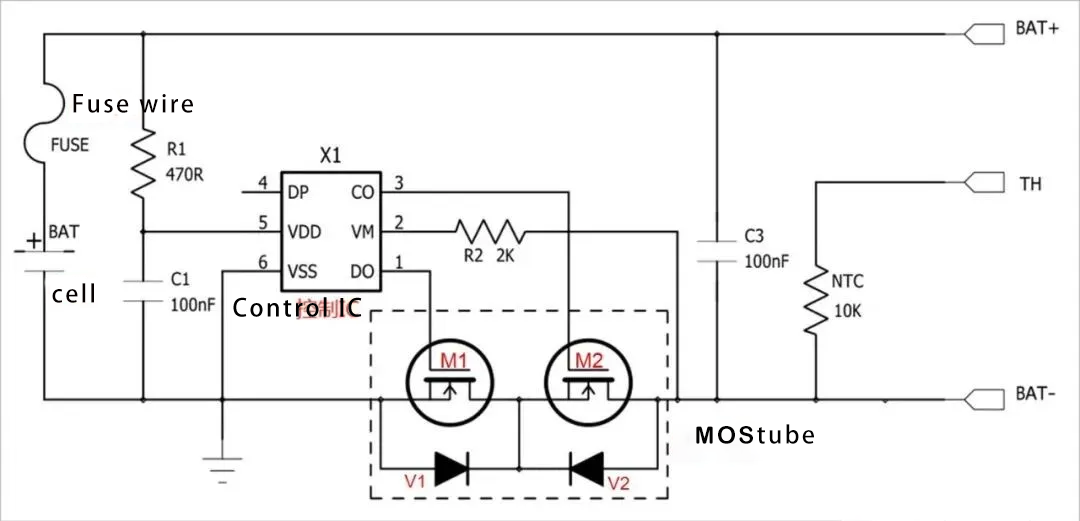
In the figure above, the control IC controls the MOS switch to achieve circuit on-off and off to protect the circuit, and FUSE realizes secondary protection on this basis; TH is temperature detection, and the inside is a 10K NTC; NTC mainly realizes temperature detection; TVS is mainly used to suppress surges.
primary protection circuit
The control IC above is responsible for monitoring the battery voltage and loop current and controlling the switching of the two MOS. Control ics can be specifically divided into AFE and MCU:
Active Front End (AFE) is the sampling chip of the battery, which is mainly used to collect the voltage and current of the battery cell.
MCU (Microcontroller Unit, microcontroller chip) mainly calculates and controls the information collected by AFE.
The relationship between the two is shown in the figure:
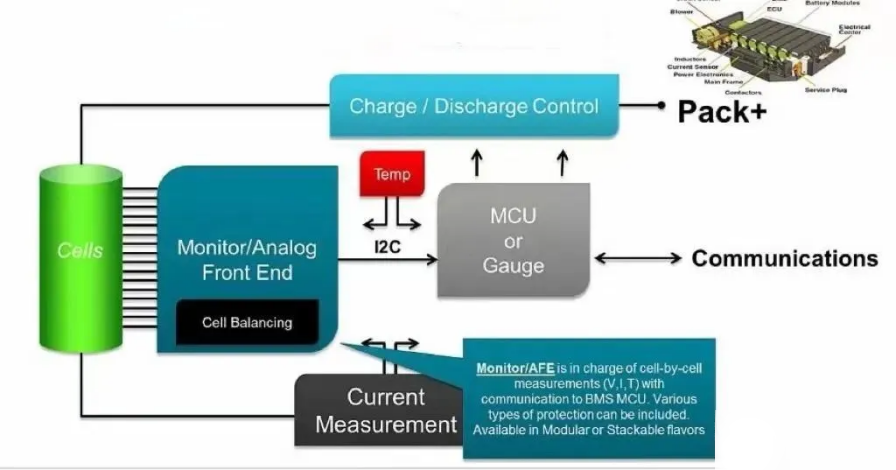
AFE
AFE is generally a 6-pin chip, CO, DO, VDD, VSS, DP and VM, which is introduced as follows:
CO: charge output;
DO: discharge output;
VDD: The power supply voltage, also known as the output voltage, is the highest voltage;
VSS: reference voltage, where the voltage is lowest;
VM: Monitors the voltage at both ends of the MOS.
When BMS is normal, CO, DO, and VDD are high, and VSS and VM are low. When any parameter of VDD, VSS, and VM is changed, the level of CO or DO will change.
MCU
MCU refers to the micro control unit, also known as the single chip microcomputer, with high performance, low power consumption, programmable, high flexibility. It is widely used in consumer electronics, automobile, industry, communication, computing, home appliances, medical equipment and other fields.
In BMS, the MCU acts as the brain, capturing all the data from the sensors through its peripherals and processing the data to make appropriate decisions based on the battery pack's profile.
The MCU chip processes the information collected by the AFE chip and plays the role of calculation (such as SOC, SOP, etc.) and control (MOS off, on-off, etc.), so the battery management system has high performance requirements for the MCU chip. AFE and MCU protect the circuit by controlling MOS.
MOS
MOS is the abbreviation of Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor field-effect Transistor, referred to as the Field Effect Transistor, which acts as a switch in the circuit, controlling the on-off and off-off of the charging circuit and discharge circuit respectively.
Its on-resistance is very small, so its on-resistance has little effect on the performance of the circuit. Under normal conditions, the consumption current of the protection circuit is μA, usually less than 7μA.
The realization of BMS first-level protection: control IC and MOS linkage
If the lithium battery is overcharged, overdischarged or overflowed, it will lead to chemical side reactions inside the battery, which will seriously affect the performance and service life of the battery, and may produce a large amount of gas, so that the internal pressure of the battery will increase rapidly, and finally lead to the pressure relief valve opening, and the electrolyte ejections occur thermal runaway.
In the case of the above, BMS will turn on the protection mechanism and do as follows:
Normal state
In the normal state, the "CO" and "DO" pins in the circuit output high levels, the two MOS are in the on-state, and the battery can be freely charged and discharged.
Overcharge protection
When charging, AFE will always monitor the voltage between pin 5 VDD and pin 6 VSS, when this voltage is greater than the overcharge cut-off voltage, MCU will turn off the MOS tube M2 by controlling pin 3 CO(CO pin from high level to low level) : then the charging loop is cut off, and the battery can only discharge. At this time, due to the presence of the body diode V2 of the M2 tube, the battery can discharge the external load through the diode.
Over-discharge protection
When discharging, AFE always monitors the voltage between pin 5 VDD and pin 6 VSS. When this voltage is less than the overdischarge cut-off voltage, MCU will turn off MOS tube M1 through pin 1 DO(DO pin changes from high level to low level), then the discharge loop is cut off and the battery can only be charged. At this time, due to the existence of the body diode V1 of the MOS tube M1, the charger can charge the battery through the diode.
Overcurrent protection
In the normal discharge process of the battery, when the discharge current passes through two MOS in series, a voltage will be generated at both ends due to the on-impedance of the MOS. The voltage value U=2IR, R is the on-impedance of a single MOS. The AFE pin 2 VM will monitor the voltage value at any time. When the loop current is large enough to make the voltage U greater than the overcurrent threshold, the MCU will turn off the MOS tube M1 through the first pin DO(the DO pin will change from high level to low level), and the discharge loop will be cut off, so that the current in the loop will be zero and play the role of overcurrent protection.
Short circuit protection
Similar to the working principle of overcurrent protection, when the loop current is large enough to make the voltage U instantly reach the short-circuit threshold, the MCU will close the MOS tube M1 through the first pin DO(DO pin changes from high level to low level), cut off the discharge circuit, and play a short-circuit protection role. The delay time of short-circuit protection is extremely short, usually less than 7 microseconds.
Two-stage protection circuit: three-end Fuse
For security reasons, a secondary protection mechanism still needs to be added. At the current stage, the application of REP (Resistor Embedded Protector) is higher, and the three-end Fuse is more cost-effective.
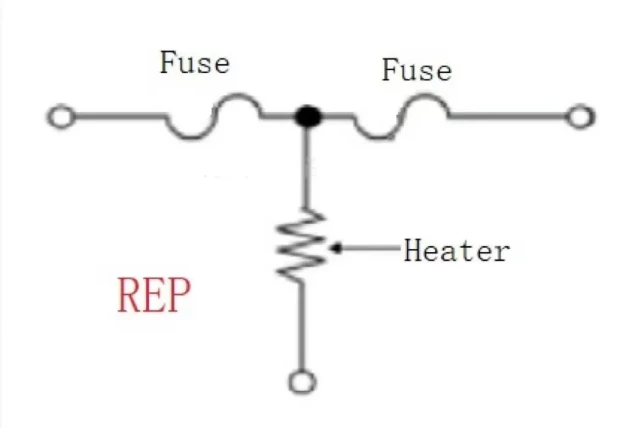
When the current is too large, Fuse and ordinary fuse principle, will be blown; When MOS runs abnormally, the three-end fuse of the main control will be blown actively. The advantages of this security protection mechanism are mainly low power consumption, fast reaction speed, good protection effect, and high application at this stage, which has been widely used in electric vehicles, mobile phones and other devices.
Three-level protection circuit: NTC and TVS
NTC thermistor
Thermistor, as its name suggests, is extremely sensitive to heat and is a kind of variable resistor, mainly divided into PTC and NTC two kinds.
PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient thermistor), the higher the temperature, the greater the resistance, mainly used in mosquito killers, heaters and other products.
NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient thermistor) in contrast to PTC, the higher the temperature, the lower the resistance, mainly used as a resistance temperature sensor and current limiting device.
Lithium battery BMS generally use NTC, compared with the product power consumption is small, high accuracy and rapid response, mainly has three functions.
Temperature measurement
Using the characteristics of the resistance, the following three temperature categories can be measured:
Cell temperature: The NTC thermistor is placed between cells to achieve cell temperature measurement, which needs to consider the number of cells covered by each NTC.
Power temperature: The NTC thermistor is placed between the MOS to achieve the measurement of power temperature, and it is necessary to ensure that the NTC is in close contact with the MOS device during installation.
Ambient temperature: Place the NTC thermistor on the BMS board to measure the ambient temperature. The installation position must be far away from the power device.
Temperature compensation
The resistance of most components will increase with the rise of temperature, at this time, NTC needs to be compensated to offset the error caused by temperature.
Inhibit surge current
electrical surge, also known as a surge, is an instantaneous peak that exceeds the stable value, including surge voltage and surge current. The electronic circuit will produce a large surge current when it is turned on, which is easy to cause damage to the components. The use of NTC can prevent this situation and ensure the normal operation of the circuit. For surge protection, TVS is needed.
TVS transient voltage suppressor
TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressors) are transient voltage suppressors, which have high response speed and are suitable for port protection. The specific implementation is as follows:
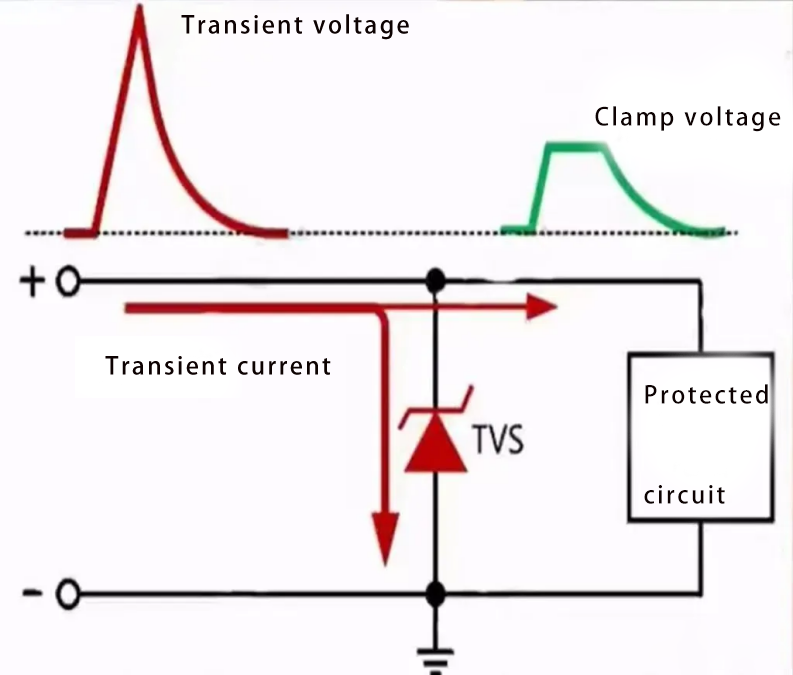
When abnormally high voltage occurs in the circuit, TVS will quickly adjust the resistance state, release the instantaneous current to the ground, and protect the rear circuit from damage; TVS will recover after the abnormal voltage situation is over.

Home energy storage product series
A lithium battery pack for home energy storage systems, which is compatible with solar panels and the sun The inverter can work together with the power grid to power household appliances, and it can also be used as a For off grid systems.
Extended reading
EMS development trend
EMS development trend Technological innovation With the continuous progress of...
THE ESSC Brand promise
Global supply
Our products sell well all over the world, covering many countries and regions, through the global logistics network, to provide customers with convenient purchasing experience.
Rigorous quality
We adhere to the highest quality control standards to ensure every product meets industry regulations and customer expectations, earning trust through consistent excellence.
Excellent service
With a customer-centric approach, we provide prompt responses, professional support, and personalized services, aiming to deliver the best user experience and long-term value.